Mastering the Binomial Theorem: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction – Understanding the Binomial Theorem
The Binomial Theorem provides a systematic method to expand expressions of the form (a + b)n. Instead of multiplying the expression repeatedly, this theorem allows for a direct calculation of each term using coefficients. It is a cornerstone concept in algebra, combinatorics, and probability, making complex polynomial expansions manageable.
Understanding the Binomial Theorem simplifies calculations, clarifies patterns in powers of binomials, and provides a foundation for higher-level mathematics. It transforms seemingly complicated expressions into structured, predictable terms.
In this guide, we will explore the theorem step by step, explain its formulas, provide examples, and demonstrate real-life applications.
Historical Background – Origins and Evolution
The Binomial Theorem has a rich history dating back to ancient mathematics, with contributions from mathematicians like Isaac Newton in the 17th century. Newton generalized the theorem to work for any exponent, including fractions and negative numbers, extending its applicability beyond integers.
Earlier forms were observed in combinatorics and algebraic patterns, including work by Persian mathematician Al-Karaji. Over time, the theorem became a critical tool for solving polynomial equations, analyzing probabilities, and understanding numerical patterns in mathematics.
Understanding this historical context highlights how the Binomial Theorem evolved into a fundamental concept that bridges classical mathematics with modern applications.
See also: Essentials Hoodie Designed for the Bold, Worn by the Everyday American
Binomial Formula – Core Concept
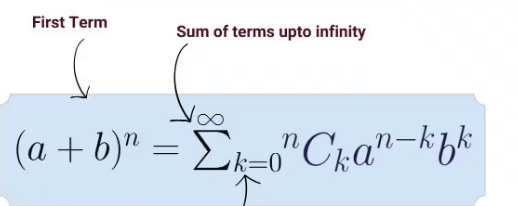
The core formula of the Binomial Theorem is:
(a + b)n = Σk=0n C(n, k) an-k bk
Here, C(n, k), also written as n choose k, represents the binomial coefficient, calculated as:
C(n, k) = n! / (k!(n – k)!)
This formula shows how each term in the expansion is constructed using coefficients, powers of a, and powers of b. By applying this systematically, you can expand any binomial expression accurately and efficiently.
Grasping the binomial formula is the foundation for understanding coefficients, expansions, and real-life applications of the theorem.
Binomial Coefficients – Understanding the Numbers
Binomial coefficients determine the value of each term in a binomial expansion. Represented as C(n, k) or “n choose k,” these coefficients are calculated using factorials: C(n, k) = n! / (k!(n – k)!). They indicate how many ways k elements can be chosen from a set of n elements.
For example, in expanding (a + b)3, the coefficients are 1, 3, 3, 1. These numbers correspond to the number of combinations for each term and also appear naturally in Pascal’s Triangle. Understanding coefficients ensures accurate calculation of each term in any expansion.
Mastering binomial coefficients is essential for predicting term values, simplifying calculations, and applying the theorem to practical problems in algebra and combinatorics.
Expansion Examples – Step-by-Step
Practical examples illustrate how the Binomial Theorem works. For instance:
- (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2
- (x + y)3 = x3 + 3x2y + 3xy2 + y3
- (2x + 3y)4 = 16x4 + 96x3y + 216x2y2 + 216xy3 + 81y4
Each term is calculated by multiplying the appropriate binomial coefficient with the respective powers of a and b. Step-by-step expansion helps visualize how the formula translates into actual terms and ensures accuracy in computations.
Working through examples reinforces understanding of coefficients, powers, and the systematic approach required to expand any binomial expression.
Applications in Probability and Statistics
The Binomial Theorem is not only a tool for algebra but also plays a key role in probability and statistics. It is used to calculate probabilities in binomial distributions, which model scenarios with two possible outcomes: success or failure.
For example, the probability of getting exactly k heads in n coin tosses is determined using the binomial formula: P(X = k) = C(n, k) * pk * (1-p)n-k, where p is the probability of success. Understanding these applications bridges algebraic concepts with real-world problems, including finance, risk analysis, and experimental probability. To make such calculations faster and more accurate, you can explore this ultimate guide to using online calculators. By mastering the Binomial Theorem, you gain tools to solve both algebraic problems and probabilistic scenarios efficiently.
Real-Life Applications – Beyond Algebra
The Binomial Theorem has practical applications beyond classroom algebra. In finance, it helps calculate compound interest and investment growth. In computer science, it aids algorithm analysis and coding problems. In physics and chemistry, it models combinations, probabilities, and reaction outcomes.
For example, understanding combinations in chemical reactions or computing probabilities of multiple events relies on binomial expansions. These applications show that the theorem is not just theoretical – it provides solutions to real-world numerical challenges.
By seeing the theorem in context, learners appreciate its relevance and can apply it strategically in diverse fields.
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls
While applying the Binomial Theorem, students often make avoidable mistakes. Common errors include miscalculating factorials, using incorrect binomial coefficients, skipping terms, or misapplying powers of a and b. Sign errors are particularly frequent in expansions involving subtraction.
For instance, expanding (a – b)4 requires careful attention to alternating signs. Awareness of these pitfalls allows learners to double-check work, ensure accuracy, and avoid compounding errors in larger problems.
Recognizing and addressing common mistakes enhances confidence and ensures that mastery of the theorem is accurate and reliable.
Tools and Resources for Mastery
Using calculators, online solvers, and tutorials simplifies the application of the Binomial Theorem. These tools help compute coefficients, expand expressions, and verify answers quickly. They are especially helpful for complex expansions or high exponents.
For example, CalculatorPoint.net provides reliable calculators for binomial expansions, factorial computations, and term verification. Using these resources reduces errors and allows learners to focus on understanding concepts rather than manual computation.
Leveraging available tools and resources accelerates learning, reinforces accuracy, and builds confidence in mastering the theorem.